

Studies have already proved that, the plants grown in space in microgravity have a greater mitotic index than plants grown on the ground. Mitotic index is used to quantify the differences in cell division when environmental parameters are changed. The meristematic region in the root tip is the actively growing region and thus the mitotic index is high. That means gradual decrease in cell division as it moves from the zone of cell division to the zone of cell elongation. Mitotic index decreases with increasing distance from root tip. Mitotic index helps us to quantify the cell division. This will help to identify the region of most mitotic activities. of cells in the dividing phase to the total number of cells observed. The percentage of cells undergoing mitosis or it is defined as the ratio of no. The super coiled chromosomes during different stages of mitosis present in the onion root tip cells can be visualized by treating with DNA specific stains, like Feulgen stain and Acetocarmine stain. The onion root tips can be prepared and squashed in a way that allows them to be flattened on a microscopic slide, so that the chromosomes of individual cells can be observed easily. An onion root tip is a rapidly growing part of the onion and thus many cells will be in different stages of mitosis. The most commonly used root tips in labs to study mitosis are onion, wheat, lentil, barley and alfalfa. Cell division occurs rapidly in growing root tips of sprouting seeds or bulbs. Walther Flemming studied and named the process of cell division as mitosis. Nägeli first saw chromosomes and in 1888 W.
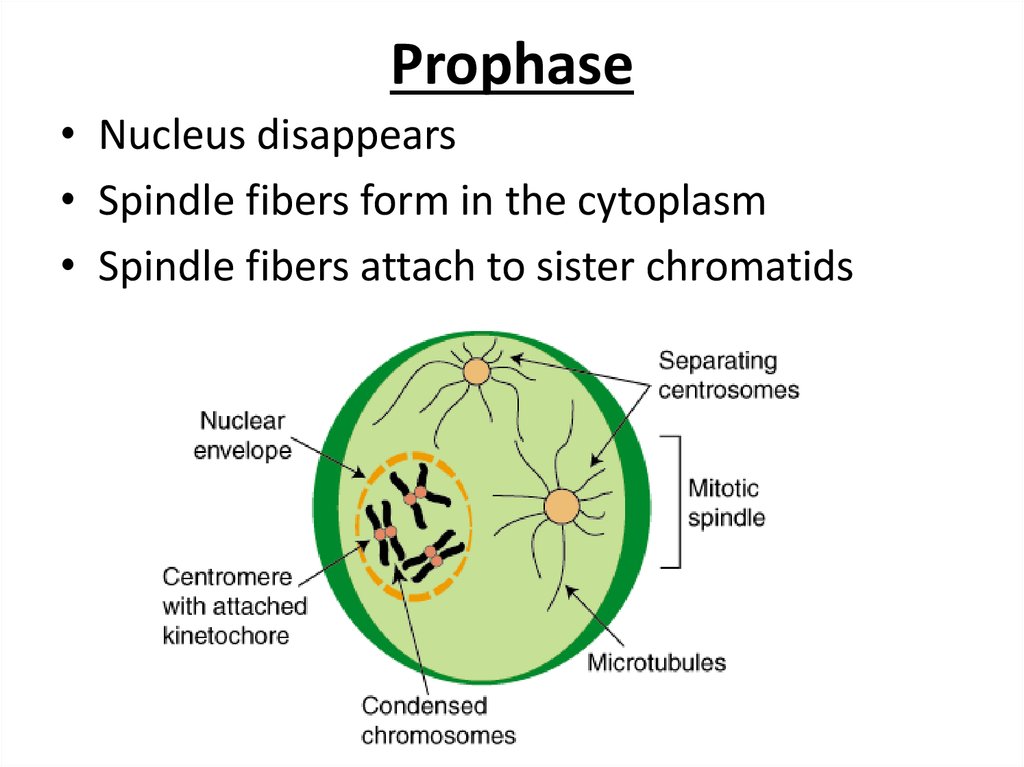
An onion cell possesses eight chromosomes lwhereas human cells possess forty six chromosomes. The genetic information of all organisms resides in the individual DNA molecules or chromosomes. The cell plate (new cell wall) starts to form between the two daughter nuclei. Telophase: During this stage, the chromosomes are clustered on the either end of the cell. The nuclear membrane disintegrates completely.Īnaphase: During this stage, the centromeres start splitting and the sister chromatids begin to migrating towards the opposite poles of the cell. The chromosomes align along the center plane of the cell. Metaphase: During this stage, the spindle fibers reach and attach to centromere of each sister chromatids. The nuclear membrane starts disintegrating. Prophase: During this stage, the chromosomes super coil, condense and become visible for first time during the cell cycle. The process of Mitosis is divided into four stages: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase. In eukaryotes, DNA replication is followed by a process called mitosis which separates the chromosomes in its cell nucleus into two identical sets, in two individual nuclei. M phase of the cell cycle stands for Mitosis or nuclear division. These phases also have certain check points and the whole cell cycle is strictly regulated. G1 and G2 are the two gap phases during which the cell grows, producing proteins and preparing the cells. Interphase is mainly divided into three phases: G1 phase, S phase and G2 phase. This is a period of diverse activities and these activities are a prerequisite for the next mitotic phase. During this phase the cell prepares for its next stage. Interphase is the longer period of cell division. Cell cycle is mainly classified into two segments: M-phase and Interphase. In normal eukaryotic cells, the type of cell division is known as mitosis.Īnother type of cell division is present in reproductive cells of eukaryotes and is known as meiosis. Cell division is a small part of the cell cycle. To visualize different phases of mitosis.Ī process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells is called cell division.To understand the process and different stages of mitosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
